The Ultimate Guide to Business Software for Startups
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, startups face unique challenges that necessitate the adoption of effective business software solutions. As new enterprises emerge, they must navigate an array of tasks ranging from project management and customer relationship management to financial tracking and marketing automation. The strategic use of such software not only streamlines operations but also enhances productivity, allowing startups to focus their limited resources on innovations and growth. Given the importance of technology in achieving business objectives, selecting the right software tools becomes a critical factor for success. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of essential business software options tailored specifically for startups, equipping entrepreneurs with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions. By understanding the myriad of available tools and their functionalities, startups can better position themselves to thrive in increasingly competitive markets.
A. Importance of Business Software for Startups
The integration of business software is critical for startups aiming to navigate the complexities of the modern market. Such software facilitates rapid prototyping, allowing startups to experiment with innovative ideas and gather valuable user feedback efficiently. As identified in recent research, the speed at which startups can learn and adapt is directly linked to their ability to prototype effectively, a process influenced by factors including artifacts and team competence (Duc A et al.). Moreover, the availability of robust software solutions enhances operational efficiency, enabling startups to manage their resources strategically and improve collaboration among team members. This agility not only supports the refinement of product offerings but also appeals to potential investors. For instance, credible commitment from venture capitalists often hinges on the startup’s ability to demonstrate innovation and reliability, further highlighting the necessity of business software in securing funding (Hochberg et al.). Thus, the importance of business software transcends mere functionality; it is a pivotal element for sustainable growth.
II. Types of Business Software
In the rapidly evolving landscape of startups, understanding the types of business software available is crucial for fostering innovation and efficiency. Primarily, business software can be categorized into productivity tools, customer relationship management (CRM) software, and project management platforms. Productivity tools streamline day-to-day operations, enabling teams to collaborate effectively and manage tasks seamlessly. Conversely, CRM software is instrumental in managing customer interactions, enhancing service delivery, and driving sales growth. Moreover, project management platforms facilitate the tracking of project timelines and resource allocation, ultimately promoting organizational efficiency. Notably, the ability to prototype rapidly can be a significant advantage for startups, as outlined in research highlighting the importance of prototyping in refining business ideas ((Duc A et al.)). Furthermore, startups often emerge from innovation initiated by individuals seeking practical solutions, which can lead to substantial job creation and R&D investment, emphasizing the critical role of software in driving entrepreneurial success ((E J Reedy et al.)).
| Software Type | Examples | Benefits | Estimated Cost (Monthly) |
| Accounting Software | QuickBooks, FreshBooks, Xero | Streamlines financial management, simplifies tax preparation | $15 – $70 |
| Project Management Software | Trello, Asana, Monday.com | Enhances team collaboration, improves task tracking | $10 – $25 |
| Customer Relationship Management (CRM) | Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM | Manages customer interactions, boosts sales | $12 – $300 |
| Email Marketing Software | Mailchimp, Constant Contact, Sendinblue | Automates email campaigns, tracks engagement | $10 – $300 |
| Human Resource Management Software | BambooHR, Gusto, Workday | Streamlines HR processes, manages employee records | $20 – $200 |
A. Overview of Essential Software Categories
In navigating the complex landscape of software applications, startups must prioritize understanding essential software categories that facilitate their business processes. Key categories include project management tools, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and prototyping software, which collectively enhance organizational efficiency and user engagement. For instance, the integration of prototyping tools is crucial, as startups often rely on rapid development cycles to iterate their offerings based on user feedback. As highlighted in the research, how fast startups can learn depends on how fast they can prototype (cite5), underscoring the importance of a structured approach towards refining product concepts. Additionally, leveraging communities of practice can be beneficial, particularly in fostering collaboration among team members involved in software innovation. These dynamics not only promote collective problem solving but also enhance the overall learning curve within startups (cite6), ultimately paving the way for sustained growth and adaptability in competitive markets.
III. Choosing the Right Software
Selecting the right software is a pivotal decision that can significantly impact the trajectory of a startup. A suitable technology solution not only streamlines operations but also enhances product development and quality, thereby preventing costly missteps that could drain valuable resources. As highlighted in recent studies, the decision-making process in digital startups is influenced by various characteristics, such as team competence and collaboration, which function as both facilitators and barriers in prototyping activities (Bohn et al.). Efficient prototyping allows startups to quickly validate ideas and gather user feedback, thus fostering a prototype-centric learning model that is crucial in the early stages of development (Duc A et al.). By understanding these dynamics, startups can make informed software choices that align with their innovation goals, ensuring a more agile response to market demands while optimizing their limited resources.
A. Factors to Consider When Selecting Business Software
In the dynamic landscape of startups, selecting appropriate business software is pivotal for operational success and scalability. One critical factor to consider is the softwares adaptability to evolving business needs; as startups grow, they may require more complex functionalities that can be met by scalable software solutions. Additionally, the integration capabilities of the software are essential, enabling seamless interactions with existing tools and systems to enhance productivity. User experience also plays a crucial role since software that is intuitive reduces training time and increases employee efficiency. Furthermore, cost is paramount, particularly for resource-limited startups, as optimizing budget allocation can significantly influence growth potential. Lastly, assessing the software’s performance in related markets can provide insights into its reliability and effectiveness, as highlighted by studies showing that successful business models often rely on digital solutions adapting to market dynamics (Bala et al.) and (Gregory J Jordan et al.).
The integration of effective business software is not merely a technical necessity for startups, but a pivotal component that significantly influences their agility and competitive advantage. As highlighted in the research, startups that prioritize rapid prototyping and embrace a learning-centric approach are better positioned for success in their early stages. By incorporating user feedback and facilitating collaborative environments, such businesses can overcome common barriers to innovation and streamline their development processes (Duc A et al.). Furthermore, academic entrepreneurship is increasingly vital, as it bridges the gap between invention and commercialization, enabling nascent ventures to harness breakthrough technologies more effectively (Roman M Lubynsky). Ultimately, this guide underscores the importance of selecting and implementing the right business software; it serves as an essential foundation for sustainable growth, innovation, and long-term viability in an increasingly dynamic market landscape.
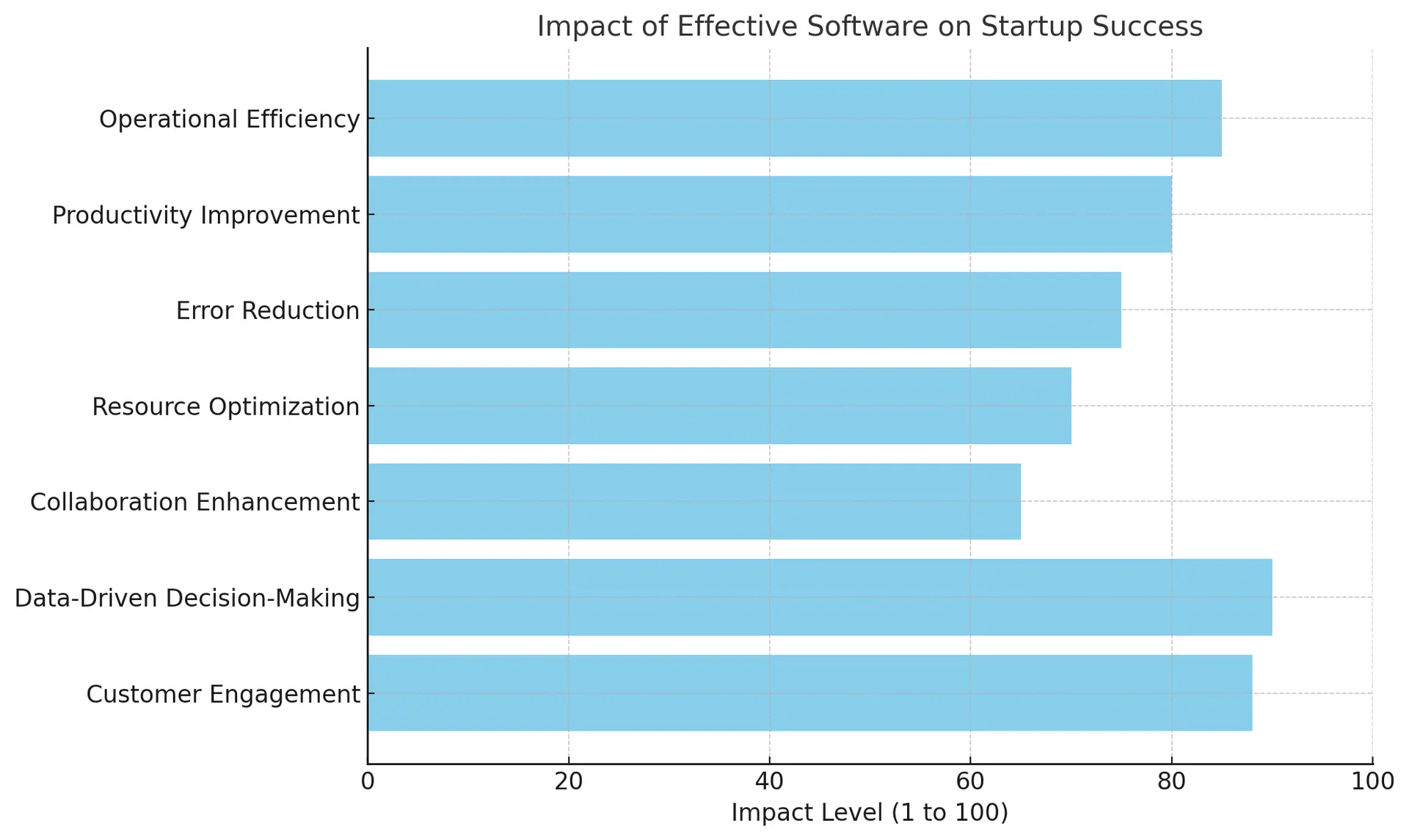
A. The Impact of Effective Software on Startup Success
In the competitive landscape of startups, effective software solutions serve as vital tools that can significantly enhance operational efficiency and productivity. Robust software platforms streamline various business processes, from project management and customer relations to financial tracking and marketing automation. By leveraging technologies that integrate seamlessly with their workflows, startups can reduce manual errors, optimize resource allocation, and foster collaboration among team members. Moreover, the right software can provide critical data insights, enabling informed decision-making and responsive strategies essential for growth. In an increasingly digital market, startups that harness effective software not only improve their internal operations but also elevate their brand presence through better customer engagement and satisfaction. Consequently, the impact of software extends beyond mere functionality; it acts as a strategic asset that can propel startups towards sustainable success, shaping their trajectory in an ever-evolving business environment.